
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, enterprises are moving beyond the first wave of digitalization and stepping into an era shaped by Artificial Intelligence (AI). This shift is not about chasing trends, but about redefining how organizations compete, operate, and grow. While technology providers may focus on hardware upgrades and infrastructure, the real transformation happens when AI is embedded into business processes and decision-making frameworks. This article explores how AI acts as a catalyst for enterprise transformation, its practical applications, and how DigiHua helps businesses make this journey a reality.
Summary
AI is no longer just a buzzword—it has become the underlying driver of enterprise competitiveness. Its value lies in four key applications: automating administrative tasks, building enterprise knowledge bases, enabling precise analytics and forecasting, and supporting managerial decision-making. However, the true impact comes only when AI is integrated into a structured transformation path: starting with data governance, advancing through process integration, evolving into intelligent decision engines, and culminating in organizational learning. DigiHua’s MES and APS solutions make this integration possible, turning AI from a pilot experiment into a practical force for operational excellence. In the end, AI should not be seen as a tool that replaces humans, but as a co-creation partner that empowers enterprises to achieve sustainable growth and resilience.
1. AI as the New Engine of Competitiveness
AI is no longer just a trend—it has become the underlying engine of competitiveness for enterprises worldwide. Artificial Intelligence (AI), in this context, refers to the ability of machines and software systems to perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. Over the past decade, many businesses, both in Malaysia and across the globe, have completed the stage of digitalization—the shift from paper-based or manual processes into digital formats and workflows. Now, they are entering the second stage: an era where AI-driven transformation takes the lead. Unlike simple optimization, which focuses on incremental improvements in speed or cost, AI-driven transformation involves rethinking business models, restructuring processes, and reshaping decision-making itself.
The critical question for leaders is no longer whether AI is important, but how to ensure that it truly takes root in their organizations. Without a clear strategy, AI risks becoming just another buzzword—a popular term used without meaningful impact—or worse, a superficial upgrade that adds tools without addressing deeper structural needs.
In short, AI should not be seen as a shiny add-on to existing systems, but as a catalyst that redefines how enterprises create value, compete, and grow.

2. Four Practical Applications of AI in Daily Operations
In daily business operations, AI demonstrates its value through four major application scenarios.
First, in document and administrative tasks, AI can automate routine but time-consuming activities such as generating meeting minutes, comparing contract terms, or consolidating regulatory updates. These functions are often powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP), a branch of AI that enables machines to understand and process human language with speed and accuracy.
Second, AI enables the creation of an enterprise knowledge base, which refers to a centralized system that organizes and connects information scattered across Excel files, PowerPoint slides, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platforms, and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES). By transforming fragmented data into structured and searchable assets, companies can prevent knowledge loss and ensure consistency across teams.
Third, AI strengthens data analysis and forecasting by leveraging machine learning (ML) models to identify demand patterns, predict supply chain risks, and measure production efficiency. Unlike traditional reporting tools that are retrospective, ML provides forward-looking insights that help organizations prepare for changes before they happen.
Finally, AI provides decision support for managers by enabling scenario modeling, often referred to as “what-if analysis.” This allows decision-makers to simulate different outcomes—for example, changes in raw material prices or shifts in production schedules—and evaluate the impact before committing resources.
In summary, AI’s true value goes beyond saving time or automating tasks: it lies in improving the quality, speed, and confidence of enterprise decision-making.
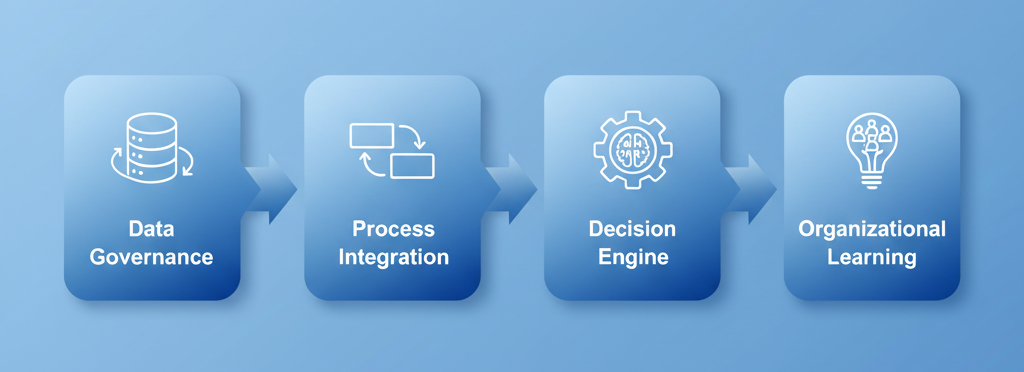
3. From Tools to Smart Operations: The Four-Step Roadmap
Moving from “AI tools” to “smart operations” requires a structured path rather than ad-hoc adoption. Enterprises can think of this journey as a four-step roadmap.
Step 1: Data governance. This means ensuring that company data is accurate, consistent, and available in real time. Without clean and reliable data, any AI model—no matter how advanced—will produce misleading or low-value outputs.
Step 2: Process integration. AI must connect with existing operational systems such as the Manufacturing Execution System (MES), which tracks and manages shop-floor activities, and the Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) system, which optimizes production capacity and supply chain resources. Integration ensures that insights generated by AI flow directly into business operations.
Step 3: Intelligent decision engine. At this stage, AI moves from a supportive role to a core driver, embedding predictive models and optimization algorithms into daily workflows. This allows organizations to act on real-time insights, creating a closed-loop cycle where decisions are continuously tested and improved.
Step 4: Organizational learning. AI adoption is not a one-off project but an ongoing process. By capturing tacit knowledge from employees and codifying it into digital systems, enterprises create intellectual capital—knowledge assets that grow over time and give them a sustainable competitive advantage.
In short, the transformation from isolated AI tools to smart operations depends on following this roadmap, ensuring that technology is not only adopted but embedded into the DNA of the organization.
4. DigiHua’s Role: Embedding AI into MES and APS
At this point, the question is not whether AI can create value, but how to make it truly work in the manufacturing environment. This is where DigiHua plays a critical role.
Through its Manufacturing Execution System (MES), DigiHua ensures that every piece of production data—from machine performance to operator inputs—is captured in real time. MES acts as the digital backbone of the factory, bridging the gap between physical equipment and business management systems. By doing so, it provides the clean, timely, and structured data foundation that AI requires to generate reliable insights.
Complementing MES is DigiHua’s Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) solution, which integrates AI into production planning and supply chain coordination. APS uses algorithms to simulate different scheduling scenarios, allocate resources more effectively, and anticipate disruptions such as demand fluctuations or material shortages. With AI embedded, APS becomes more than a scheduling tool; it evolves into a strategic system for resilience and agility.
Unlike standalone AI pilots that often remain disconnected from daily operations, DigiHua’s approach emphasizes embedding AI into existing enterprise systems. This ensures that AI is not an experimental add-on, but a practical catalyst that transforms routine processes into intelligent workflows.
In summary, DigiHua’s MES and APS solutions represent the bridge between AI’s potential and its real-world impact, helping enterprises move from aspiration to execution in their transformation journey.
5. AI as a Co-Creation Partner, Not a Replacement
Ultimately, AI should be seen not as a replacement for human capability, but as a co-creation partner that strengthens it. While AI excels at handling repetitive tasks, analyzing vast datasets, and generating predictive insights, it cannot define strategic priorities, interpret subtle market signals, or replicate the intuitive judgment that comes from years of human experience.
For business leaders, the real opportunity lies in redesigning the division of roles: allowing AI to take over the heavy lifting of data and process management, while enabling people to focus on creativity, collaboration, and critical decision-making. This human–AI partnership creates a cycle where technology amplifies human strengths, and human insight guides technological growth.
In conclusion, AI is not merely a hardware upgrade—it is the catalyst for enterprise transformation. By embedding AI into systems like MES and APS, companies can enhance efficiency, build resilience, and unlock new levels of decision-making quality. More importantly, they can position AI as a trusted partner that drives sustainable growth in an increasingly dynamic and competitive world.



?A-Comprehensive-Guide-1024x576.webp)
